Ten useful LibreOffice Macro Recipes
Macros are a great way to automate tasks in Spreadsheet applications, be it the good old Microsoft Excel or the equally efficient FOSS alternative, LibreOffice Calc. The best thing about macros is that they are often written in a very easy to grasp language called Basic (though Calc also supports Python these days).
As its very name suggests, Basic is a lenient programming language actually designed with ease of use in mind. For instance, upper/lower case doesn’t matter for variable names or keywords (if/IF, sub/Sub, function/Function are equivalents), function braces are optional like Ruby and type-conversion happens automatically. This makes Basic highly useful for both power users and programmers. A LibreOffice Basic macro is just a function or sub procedure which does a specific useful task. In this tutorial, we will see ten such useful macros which can help you with various automation tasks.
- Recipe 0: How to create a LibreOffice macro
- Recipe 1: Read cell contents
- Recipe 2: Change cell contents
- Recipe 3: Search and Replace text
- Recipe 4: Regular Expressions
- Recipe 5: Show File-open dialog
- Recipe 6: Show File-save dialog
- Recipe 7: File I/O: Read from files
- Recipe 8: File I/O: Write to files
- Recipe 9: Load data from a CSV file
- Recipe 10: Copy text to clipboard
- Demo
- Further Reading
Recipe 0: How to create a LibreOffice macro
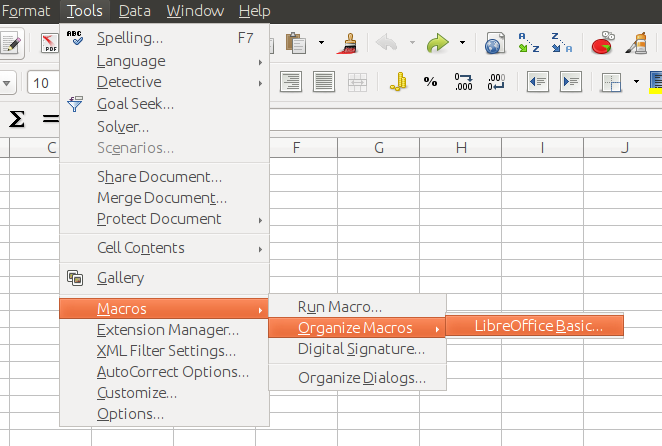
Whilst macros can be created in Writer and Draw too, in this specific tutorial, we will restrict ourselves to spreadsheets (Calc). To create a macro, just open the spreadsheet in LibreOffice and go to Tools->Macros->Organize Macros->LibreOffice Basic menu. After that, if you want to create a macro specific to your spreadsheet (as usually is the case), expand your spreadsheet file on left and select Standard and click New. This will open the LibreOffice Macro Editor as a separate window.
Recipe 1: Read cell contents
One of the most basic things needed for automation is reading a cell’s contents. The following piece of code does exactly this:
Sub read_cell
dim document as object
document = ThisComponent
sheet = document.Sheets(0)
MsgBox(sheet.getCellByPosition(0, 0).String)
End Sub
dim is a keyword used to declare a variable but declaration is totally optional unless Option Explicit is specified at the beginning of the module. ThisComponent is the LibreOffice object that references the current spreadsheet (or a written document in case of Writer). The important thing here is the expression, sheet.getCellByPosition(0, 0).String which gets the contents of first cell in the first row. Cells can be referenced using the co-ordinate system where (0,0) refers to cell at row-0 and column-0. Thus, any value across the entire spreadsheet can be fetched using this simple method.
To run a macro from the editor, just place the cursor inside the sub or function body of any macro and press F5 (or alternatively, click the Run BASIC icon on the toolbar).
Recipe 2: Change cell contents
Another often needed thing is the ability to change the cell contents. The following code sets the first cell in the first row to “Hola! Mundo”, the Spanish expression for “Hello! World”:
Sub change_cell
dim document as object
document = ThisComponent
sheet = document.Sheets(0)
sheet.getCellByPosition(0, 0).String = "Hola Mundo!"
MsgBox("Done")
End Sub
Recipe 3: Search and Replace
Searching and replacing specific strings could be an important part of your automation routine. Below is a fun macro that searches for the first names of some Linux experts (like Linus, Richard, Peter, etc.) and replaces it with their last names (Torvalds, Stallman, Anvin):
Sub replace_text
Dim names() As String
Dim surnames() As String
Dim n As Long
Dim document As Object
Dim sheets as Object
Dim sheet as Object
Dim replace As Object
names() = Array("Linus", "Richard", "Peter", "Greg", "Bill")
surnames() = Array("Torvalds", "Stallman", "Anvin", "Kroah", "Gates")
document = ThisComponent rem .CurrentController.Frame
rem sheet = doc.CurrentSelection.Spreadsheet
sheets = document.getSheets()
sheet = sheets.getByIndex(0)
replace = sheet.createReplaceDescriptor rem document.createReplaceDescriptor in case of Writer
rem replace.SearchRegularExpression = True
For n = lbound(names()) To ubound(names())
replace.SearchString = names(n)
replace.ReplaceString = surnames(n)
sheet.replaceAll(replace)
Next n
MsgBox("Done")
End Sub
names() and surnames() are actually arrays. Unlike C and Java, arrays in Basic are declared and accessed using round braces and not square ones. Also, what gets declared in an array declaration is the upper-bound, not the total size. Thus, foo(2) is actually a size-3 array ranging from indices 0 to 2.
Recipe 4: Regular Expressions
Regular expressions are very useful in searching and replacing text based on specific patterns. The following macro searches for all the email addresses in your spreadsheet and replaces each one with foo@bar.com:
Sub replace_with_regex
Dim names() As String
Dim surnames() As String
Dim n As Long
Dim document As Object
Dim sheets as Object
Dim sheet as Object
Dim replace As Object
pattern = "\b[A-Z0-9._%+-]+@[A-Z0-9.-]+\.[A-Z]{2,}\b" rem regex pattern to match any email address
document = ThisComponent rem .CurrentController.Frame
sheets = document.getSheets()
sheet = sheets.getByIndex(0)
replace = sheet.createReplaceDescriptor rem document.createReplaceDescriptor in case of Writer
replace.SearchRegularExpression = True
replace.SearchString = pattern
replace.ReplaceString = "foo@bar.com"
sheet.replaceAll(replace)
MsgBox("Done")
End Sub
Recipe 5: Show File-open dialog
Showing the File-open dialog is a very common requirement, especially when you want to open an external file for processing. The below code uses the FilePicker object to show the file-open dialog and return the selected file-name:
function show_open_dialog
dim aurl as object
dim s as string
dim oDlg as object
oDlg = createUnoService("com.sun.star.ui.dialogs.FilePicker")
oDlg.setMultiSelectionMode(false)
oDlg.appendFilter("CSV Files (.csv)", "*.csv" )
oDlg.execute
aUrl = oDlg.getFiles()
s = aUrl(0)
if len(s) > 0 then
MsgBox("File Selected: " & s & chr(13))
end if
show_open_dialog = s
end function
createUnoService is a LibreOffice specific method for creating helper objects like FilePicker in this example. The appendFilter method is used to filter out only CSV files in the dialog.
Recipe 6: Show File-save dialog
For showing a File-save dialog, the same FilePicker object is used, initializing it with the FILESAVE_AUTOEXTENSION argument:
function show_save_dialog
dim aurl as object
dim s as string
dim oDlg as object
sFilePickerArgs = Array(_
com.sun.star.ui.dialogs.TemplateDescription.FILESAVE_AUTOEXTENSION )
oDlg = createUnoService("com.sun.star.ui.dialogs.FilePicker")
oDlg.initialize(sFilePickerArgs())
oDlg.setMultiSelectionMode(false)
oDlg.appendFilter("CSV Files (.csv)", "*.csv" )
oDlg.setTitle("Save As....")
if oDlg.execute() then
aUrl = oDlg.getFiles()
s = aUrl(0)
if len(s) > 0 then
MsgBox("File Selected: " & s & chr(13))
end if
else
s = ""
end if
show_save_dialog = s
end function
Recipe 7: File I/O: Read from files
Raw file I/O is a feature provided by almost every language and Basic macros make it almost too easy. Below code is used to read a CSV file with three columns. Name of the file is set in the filename variable. The variable num is a numerical tag used to reference the file-handler and FreeFile() returns a free available number that can be used for tagging. The open statement is self-explanatory. In Basic, files can be opened in Input, Output and Binary modes. Finally, the input statement is used to actually read the file into the variables line after line.
sub file_io_read
dim v1, v2, v3
filename = "/home/prahlad/data/test.csv"
num = FreeFile()
open filename for input as #num
do while not eof(num)
input #num, v1, v2, v3
print v1 & "::" & v2 & "::" & v3
loop
close #num
msgbox "Done"
end sub
Recipe 8: File I/O: Write to files
For writing to files, a handler is opened in output mode instead of input, and the write statement is used to actually write the variables to a file.
sub file_io_write
filename = "/home/prahlad/data/dummy.csv"
num = FreeFile()
open filename for output as #num
write #num, "col1", "col2", "col3"
write #num, "1", "2", "3"
write #num, "4", "5", "6"
close #num
msgbox "Done"
end sub
Recipe 9: Load data from a CSV file
Apart from working in raw I/O mode, it is sometimes required to load a complete CSV as a sheet in the current document. Using the show_open_dialog function that we studied earlier, the following macro first prompts a user with a File-open dialog and then loads the specified CSV file as a new sheet:
sub load_from_csv
fname = show_open_dialog
if len(fname)>0 then
dim fileProps(1) as new com.sun.star.beans.PropertyValue
fileProps(0).Name = "FilterName"
fileProps(0).Value = "Text - txt - csv (StarCalc)"
fileProps(1).Name = "FilterOptions"
fileProps(1).Value = "44,34,76,1,,0,false,true,true,false"
document = StarDesktop.loadComponentFromURL(fname, "_blank", 0, fileProps())
end if
msgbox "Done"
end sub
fileProps(0) is a property variable used for specifying the CSV file format, while fileProps(1) specifies the default formatting options for the CSV (such as a delimiter, charset, etc.)
Recipe 10: Copy text to clipboard
Your custom processing might involve putting a specific text to the clipboard from LibreOffice Calc. Following code shows how to put the string “Hola!” to the system clipboard:
sub copy_to_clipboard
oClip = CreateUnoService("com.sun.star.datatransfer.clipboard.SystemClipboard")
oTR = createUnoListener("TR_", "com.sun.star.datatransfer.XTransferable")
oClip.setContents(oTR, null)
msgbox "Done"
end sub
Function TR_getTransferData( aFlavor As com.sun.star.datatransfer.DataFlavor ) As Any
If (aFlavor.MimeType = "text/plain;charset=utf-16") Then
TR_getTransferData = "Hola!"
EndIf
End Function
Function TR_getTransferDataFlavors() As Any
Dim aF As new com.sun.star.datatransfer.DataFlavor
aF.MimeType = "text/plain;charset=utf-16"
aF.HumanPresentableName = "Unicode-Text"
TR_getTransferDataFlavors = Array(aF)
End Function
Function TR_isDataFlavorSupported( aFlavor As com.sun.star.datatransfer.DataFlavor ) As Boolean
TR_isDataFlavorSupported = (aFlavor.MimeType = "text/plain;charset=utf-16")
End Function
Second function is a callback and is used for storing the string to clipboard. The last two are helper functions used by the SystemClipboard and XTransferable helper objects and are required.
Demo
Finally, the working LibreOffice Calc spreadsheet implementing all these examples can be found here.
Further Reading:
- http://api.libreoffice.org/examples/examples.html#Basic_examples
- https://forum.openoffice.org/en/forum/viewtopic.php?f=25&t=36441
- https://ask.libreoffice.org/en/question/39940/calc-open-and-save-csv-file-with-given-filter-options/
- https://wiki.openoffice.org/wiki/Documentation/DevGuide/OpenOffice.org_Developers_Guide
- https://wiki.openoffice.org/wiki/Documentation/BASIC_Guide/Cells_and_Ranges
- http://www.excel-spreadsheet.com/vba/inputoutput.htm
- https://forum.openoffice.org/en/forum/viewtopic.php?f=45&t=13783